About Application Virtualization
AdminStudio 2023 | 25.0 | Automated Application Converter
Note:This section provides a description of virtualization in general for those that are not familiar with it. It does not represent the architecture of any specific vendor.
A typical Windows application has dependencies on components that are shared by multiple applications, such as registry entries or COM controls. When an installation author recognizes that their application requires a shared component—such as MDAC (Microsoft Data Access Components)—they include a merge module to install that component.
When one of these shared components is installed during an application’s installation, it is possible that a previously-installed version of the same component could be overwritten, causing the existing application to break. Because of these possible problems, extensive compatibility testing needs to be performed before an application can be distributed in the enterprise environment. The following diagram provides an example of two conflicting installed applications.
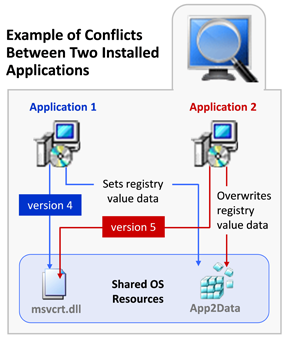
Example of Conflicts Between Two Installed Applications
Virtualization simplifies the situation by keeping the application layer and the operating system layer separate, so that the virtual application has no impact on the other applications. In application virtualization, a container or isolation environment is created around the application: a controlled virtual space for application execution that separates the interaction between an application and the underlying operating system's resources in order to protect applications from conflicting with each other.
The following diagram provides an example of how application virtualization would solve the conflicts shown in the previous example.
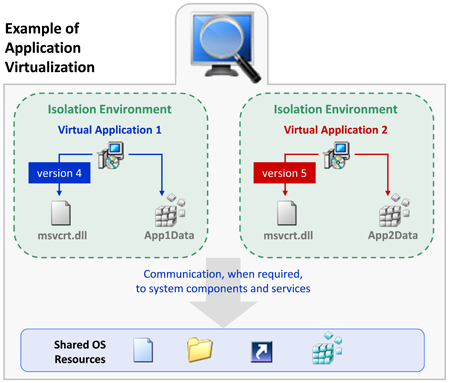
Example of Application Virtualization
Application virtualization allows the configuration of an application to be standardized to an isolation environment, rather than to an individual user’s desktop machine. Application objects, files and registry settings are contained within this isolation environment. Critical application resources are managed locally by the isolation environment, thus minimizing resource dependencies between applications.
Application virtualization greatly reduces the scope for conflicts between applications and, therefore, simplifies compatibility testing.
See Also
About Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V)