How Does IT Asset Management Calculate CAL Compliance
FlexNet Manager for Microsoft product to create and manage CALs
in IT Asset Management. To gather CAL usage inventory, you must set
CAL inventory options while creating an inventory target
to Allow CAL access evidence collection on these targets. For
more information, see Creating a Target in the online help (Discovery and
Inventory > Discovery > Discovery and Inventory Rules >
Targets > Creating a Target)..swacc) as a part of the discovery and
inventory process. This file is only generated for the inventory devices that have the
supported server products installed on Windows Server 2012 or later and for which
Microsoft’s User Access Logging (UAL) capability has been enabled. Access evidence is
collected through various services including User Access Logging (UAL) and PowerShell
scripts for some products. IT Asset Management can collect the access evidence
through any of the following methods:- The locally-installed FlexNet inventory agent
- Zero-footprint inventory collection through inventory beacon(s)
- Inventory uploads from Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (previously Microsoft SCCM) (CAL usage inventory only for Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager)
- Manual upload of access evidence through the Inventory Data One-Off Upload page.
The inventory collected from any of these sources is transferred from an inventory beacon to the central application server through regularly scheduled uploads.
For conventional device licenses, during the reconciliation process the Application Recognition Library (ARL) matches the available evidence to record an application installation. For CALs, while access evidence is linked to an application, it is not used to recognize the linked application installation; instead, it is used to identify access to that application. Like other product licenses, a CAL is also linked to the appropriate application record. However, in the case of CALs, the compliance position is generated based on the usage data (how many clients accessed the server application). The default license priorities are used to consume the appropriate license entitlement against a piece of access evidence. The collected access evidence records are visible on the Access evidence tab in the All Evidence page ().
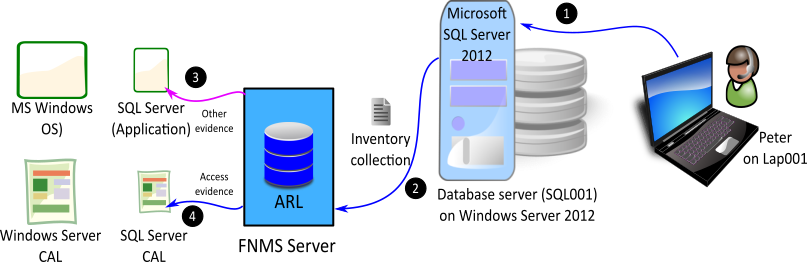
- A user Peter accesses the Microsoft SQL Server 2012 installation on SQL001 database server, installed on Microsoft Windows 2012. The access event is recorded for Microsoft Windows and Microsoft SQL Server.
- During the next inventory collection process, IT Asset Management gathers hardware, software, and access inventory for the SQL001 inventory device.
- During reconciliation, IT Asset Management uses evidence to report an installation of Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and Microsoft Windows 2012.
- The collected access evidence identifies that Peter accessed Microsoft Windows Server 2012 and Microsoft SQL Server 2012 on SQL001.
- Assuming that neither Peter nor Lap001 has already consumed a CAL for accessing any other Windows server, IT Asset Management consumes an entitlement of Microsoft User or Device CAL for each of Microsoft SQL Server and Microsoft Windows based on the set license priorities. For more details on license priorities, see the How Does License Consumption Order Work? topic in the online help.
- If you have a per-processor or per-core license for Microsoft SQL Server on SQL001, CALs are not required.
- If Peter is an outside user (for example, a consultant on a customer site), an External Connector license may also be required.
- If this Microsoft Server Installation is used by both internal and external
users, you need CALs and an External Connector license, or you can buy a
Processor or Core-based license of Microsoft SQL
Server.
If the collected access evidence does not match a known server product, it is preserved as unrecognized evidence (visible on the Unrecognized Evidence page). By default, IT Asset Management retains the CAL usage inventory data for 90 days from the date of inventory collection, unless the value of the Number of days to keep CAL usage inventory control is changed. For details, see the System Menu > System Settings > System Settings: Inventory Tab page in the online help.
Access evidence collection methods
- User Access Logging (UAL): When this access method is used, IT Asset Management collects the access evidence through the User Access
Logging (UAL) service of Windows Server, enabled by default in Windows
Server 2012 or later. This service records the client device and user
request events used to access Windows Server and other installed Microsoft
server applications (such as Microsoft SharePoint
Server) into a local database. IT Asset Management
collects the access evidence data through a PowerShell script that uses
specific Microsoft APIs for UAL. The access events are recorded for both
physical and virtual clients and servers. To use this service for a
particular Microsoft server application, the UAL service should be enabled
on the host Windows Server. The accessed server application should be
registered with the UAL service (as happens automatically during
installation). For more information about enabling the UAL service, see
Microsoft documentation for the
Get-Service UALSVCPowerShell cmdlet. For more information about products registered with UAL, see Microsoft documentation for theGet-UALOverviewPowerShell cmdlet.The appropriate inventory beacon automatically runs specific scripts to determine which user accessed which server over the last 90 days, and through which inventory device. These scripts are run as a part of the discovery and inventory process.
- PowerShell: When this access method is used (for Microsoft Exchange
and Microsoft Skype for Business), IT Asset Management collects access
data using a PowerShell script that uses specific Microsoft APIs to track
the server applications accessed by users. This data is collected as a part
of the discovery and inventory process. The following details are not
imported when this method is used:
- Accessing device
- Access date
- Access count.
Note: IT Asset Management only gets the accessing user details (who accessed the server product) and not the accessing device details (the device through which the server product was accessed). These details are specific only to the date and time when inventory was collected, and not for the last 90 days. Therefore, Device CALs are not supported for this method. Also, when a supported server application (such as Microsoft Exchange, SharePoint, or Skype for Business) is installed on versions of Microsoft Windows Server prior to Microsoft Windows Server 2012 (for example, Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003 and earlier), the server application will not have UAL support. In these instances, for each access to the supported server application, IT Asset Management creates an access evidence record for Microsoft Windows Server too. This is because a User or Device CAL for Microsoft Windows is also required, in addition to a User or Device CAL for the accessed server application. - SCCM Adapter: The SCCM adapter has been enhanced to collect the access evidence for Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (previously Microsoft SCCM) accesses. The operator can create the corresponding core CAL license in IT Asset Management.
- Spreadsheet imports: You can download the CAL usage inventory
template, populate it with evidence data, and upload it to create access
evidence records. This method is recommended when you cannot collect access
evidence. For example, when UAL service is disabled, or for servers running
versions of Microsoft Windows Server prior to Microsoft Windows Server 2008
(with no UAL support). You can also use the
CAL Legacylicense type for manual management of CALs. For more information about spreadsheet imports, see the Importing Inventory Spreadsheets and CSV Files chapter of this guide.
CAL consumption mode
- Consume entitlements based on Access: If you set the consumption mode
to Access, IT Asset Management consumes a User
CAL for all the users listed on the All IT Asset Users page (), or a Device CAL for all the devices listed on the All Inventory page (), unless any restrictions are applied through the
Restrictions tab of the license properties. If
you restrict the scope of this license to a specific enterprise group, a CAL
is consumed for each user (in case of User CALs) or each device (in case of
Device CALs) that are members of that enterprise group. For more information
on license consumption restrictions, see the online help.Note: No access evidence is required when entitlements are consumed based on access.
- Consume entitlements based on Usage within the time limit: If you set the consumption mode to Usage, IT Asset Management consumes User or Device CAL for users or devices whose access to a server application has been reported by the appropriate access evidence. Usage tracking must be enabled for the accessed application.
Supported server products for CAL management
| Microsoft Product | Product Version | User CALs Consumption | Device CALs Consumption | Inventory Data Source | Notes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Access based | Usage based | Access based | Usage based | User CAL | Device CAL | |||
| Windows Server | 2012 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | |
| 2012 R2 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | ||
| 2016 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | ||
| 2019 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | ||
| 2022 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | ||
| SQL Server | 2012 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later |
| 2014 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2016 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2017 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2019 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2022 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| Exchange Server | 2010 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | |
| 2013 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| 2016 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| 2019 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| SharePoint Server | 2010 | Full | Limited | Full | Partial | Spreadsheet Import | Spreadsheet Import | |
| 2013 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2016 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| 2019 | Full | Full | Full | Partial | UAL | UAL | Supported only on Windows Server 2012 or later | |
| Skype for Business (Lync) | 2010 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | |
| 2013 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| 2015 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| 2019 | Full | Partial | Full | Limited | PowerShell | Spreadsheet Import | ||
| Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager (previously Microsoft SCCM) | 2012 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory |
| 2012 R2 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 1511-1906 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 1910 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2002 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2006 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2010 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2103 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2107 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2111 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2203 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2207 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2211 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2303 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
| 2309 | Full | Full | Full | Full | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager | Requires Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager inventory | |
- Full: Full support (UAL user data or Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager data)
- Partial: Partial support (PowerShell script data or UAL device data)
- Limited: Limited support (requires spreadsheet import of access or usage data)
UAL service of Microsoft Windows has been enabled on each
accessed server. The accessed server application should be registered with the
UAL service (which happens automatically during installation).Application usage versus CAL usage
It is important to understand the difference between application usage and CAL usage. In the above diagram, Microsoft SQL Server 2012 is an application installed on the server and recognized by IT Asset Management through imported evidence. When this application is accessed by a user (such as the database administrator) or another application installed on SQL001 device, the application usage is recorded for Microsoft SQL Server. The usage record is linked to the inventory device record of the physical server where the database has been installed.
When the service of this instance of Microsoft SQL Server is requested through a client device (for example, Lap001), the access event is recorded (by Microsoft UAL service) and collected for Microsoft SQL Server as CAL usage. The same process is used for Microsoft Windows 2012 on SQL001.
IT Asset Management (Cloud)
Current