Creating Calculated Measures in Insights
Note:
In Data Explorer, you can create your own calculated measures from the measures already available in your insights using basic arithmetic functions.
You can create new calculated measures from:
| • | Measures, calculated measures, and attributes that you add to the Measures section from the Data Catalog. |
| • | Derived measures created using the time over time comparison. For details, see Time Over Time Comparison. |
| • | Already created calculated measures. |
The following table lists all available functions:
|
Function |
Expression |
Example |
Default Format |
|
Sum |
A+B |
Sum of A and B |
##.## |
|
Difference |
A-B |
Difference of A and B |
##.## |
|
Product (Multiplication) |
A×B |
Product of A and B |
##.## |
|
Ratio |
A÷B |
Ratio of A and B |
##.## |
|
Change |
(A-B)÷B |
Change from B to A |
##.##% |
Calculated measures depend on the measures that are used to create them. If you delete an item used to create the calculated measure, Data Explorer deletes the calculated measure as well. Also, if you switch to an insight type that cannot display measures used to create the calculated measure, the calculated measure is hidden.
Note:Calculated measures are available only in the insights where you create them—Data Explorer does not save these calculated measures to the Data Catalog. To use them elsewhere, create the calculated measures again in another insight.
Refer to the following subsections on this page for additional information:
| • | Naming Calculated Measures |
| • | Comparing Calculated Measures Over Time |
| • | Creating Calculated Measures Using Arithmetic Functions |
| • | Deleting Calculated Measures |
| • | Example |
Data Explorer creates an automatic name for calculated measures. The name consists of the name of the function and measures used. For example, Difference of Emails Sent and Emails Delivered. For details about changing the name, see Renaming Measures.
Comparing Calculated Measures Over Time
You can compare calculated measures over time as any regular measure. For details, see Time Over Time Comparison.
Calculated measures from measures already derived from time over time comparison cannot be compared over time again.
Creating Calculated Measures Using Arithmetic Functions
To create calculated measures using arithmetic functions:
| 1. | In Data Explorer, create an insight with at least two items in the Measures section. |
| 2. | In the Measures section, hover your mouse over the plus sign and click Create Calculated Measure. |

| 3. | In the Outcome is dropdown menu, select the function that you want to use to calculate the new measure. |
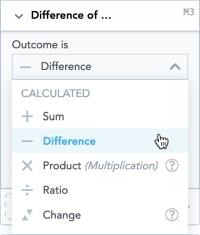
| 4. | In the Where section, click Choose Measure and select a measure from the list of available items for both parts of the function (A and B). The measures and attributes you select are highlighted above in the Measures section. |

Data Explorer adds a new measure to the Measures section and displays it in the insight.
For a sample insight with calculated measure, see the Example below.
If you create calculated measures in an insight, the Open as Report button is disabled
To delete calculated measures, drag them to the Data Catalog.
If you remove any measure that is part of the calculated measure, the calculated measure and measures derived from it are also removed.
When you drag the measure to the Data Catalog, Data Explorer highlights all the measures to be deleted and then displays a message.

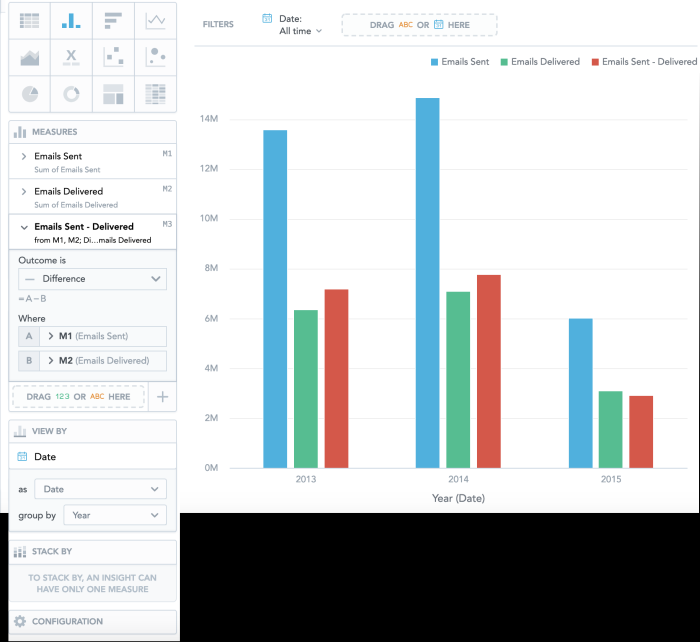
You send regular emails to your customers. You want to know how many of these emails are not delivered to the customers' inboxes each year.
Your Data Catalog includes the following data:
| • | The number of emails you sent to your customers (Emails Sent) |
| • | The number of emails that were actually delivered (Emails Delivered). |
You can use these two measures to calculate the number of emails that customers did not receive.
| 1. | Drag Emails Sent and Emails Delivered to the Measures section. |
| 2. | Add Date to the View by section and group by Year. |
| 3. | Click Create Calculated Measure and select: |
| a. | Difference as the Outcome |
| b. | Emails Sent as M1 |
| c. | Emails Delivered as M2. |
The following image shows the final insight.